ISO 45001 is the international standard for occupational health and safety (OH&S) management systems. Whether you're pursuing formal certification or simply want to implement best practices, this guide walks you through everything you need to know to build an effective OH&S management system.
What is ISO 45001?
ISO 45001:2018 is the first truly global international standard for occupational health and safety. Published in March 2018, it replaced OHSAS 18001 and provides a framework for organisations to proactively improve their OH&S performance by:
- Preventing work-related injury and ill health
- Providing safe and healthy workplaces
- Eliminating hazards and minimising OH&S risks
- Continually improving the OH&S management system
The standard follows the same high-level structure (HLS) as other ISO management system standards like ISO 9001 (Quality) and ISO 14001 (Environmental), making it easier to integrate multiple management systems.
OHSAS 18001 was withdrawn in March 2021. If your organisation was certified to OHSAS 18001, you should have already migrated to ISO 45001. The good news is that ISO 45001 builds on many of the same principles.
Benefits of ISO 45001 Certification
Implementing ISO 45001 delivers both tangible and intangible benefits:
Reduced Incidents
Systematic hazard identification and risk control leads to fewer workplace injuries and illnesses.
Cost Savings
Lower insurance premiums, reduced compensation claims, and less downtime from incidents.
Legal Compliance
Structured approach to identifying and meeting legal requirements reduces compliance risk.
Worker Engagement
Emphasis on consultation and participation improves morale and safety culture.
Competitive Advantage
Certification demonstrates commitment to safety, often required for tenders and contracts.
Continual Improvement
Built-in mechanisms ensure your OH&S performance keeps getting better over time.
Structure of the Standard
ISO 45001 follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle and is organised into 10 clauses. Clauses 1-3 are introductory, while clauses 4-10 contain the requirements:
Context of the Organisation
Understanding your organisation, stakeholders, and defining the scope of your OH&S management system.
Leadership and Worker Participation
Top management commitment, OH&S policy, roles and responsibilities, and worker consultation.
Planning
Addressing risks and opportunities, hazard identification, legal requirements, and OH&S objectives.
Support
Resources, competence, awareness, communication, and documented information.
Operation
Operational planning and control, emergency preparedness and response.
Performance Evaluation
Monitoring, measurement, analysis, internal audit, and management review.
Improvement
Incident investigation, nonconformity, corrective action, and continual improvement.
Clause 4: Context of the Organisation
Before building your management system, you need to understand the context in which it operates:
4.1 Understanding the Organisation
Identify internal and external issues that affect your ability to achieve OH&S objectives:
- External: Economic conditions, industry trends, regulatory environment, technology changes
- Internal: Culture, structure, capabilities, existing systems and processes
4.2 Understanding Stakeholder Needs
Identify interested parties and their relevant requirements:
| Interested Party | Example Requirements |
|---|---|
| Workers | Safe working conditions, consultation on safety matters, training |
| Regulators | Compliance with health and safety legislation |
| Customers | Safe products/services, contractor safety requirements |
| Insurers | Risk management, incident reporting, safety standards |
| Contractors | Clear safety requirements, coordination, site inductions |
4.3 & 4.4 Scope and Management System
Define the boundaries of your OH&S management system, considering:
- Physical locations and activities covered
- Products, services, and processes included
- Any exclusions (must be justified)
Start with a manageable scope—you can always expand later. It's better to have a well-implemented system covering part of your organisation than a poorly implemented one trying to cover everything.
Clause 5: Leadership & Worker Participation
ISO 45001 places strong emphasis on leadership commitment and worker involvement—more so than its predecessor OHSAS 18001.
5.1 Leadership and Commitment
Top management must demonstrate leadership by:
- Taking overall responsibility and accountability for OH&S
- Ensuring the OH&S policy and objectives are established and compatible with strategic direction
- Ensuring integration of OH&S requirements into business processes
- Ensuring resources are available
- Promoting continual improvement
- Supporting other relevant management roles
5.2 OH&S Policy
Your OH&S policy must include commitments to:
- Provide safe and healthy working conditions
- Eliminate hazards and reduce OH&S risks
- Comply with legal and other requirements
- Consult and participate with workers
- Continually improve the OH&S management system
5.4 Worker Participation and Consultation
A key difference from OHSAS 18001 is the emphasis on worker participation:
Consultation
Seeking views before making decisions about:
- Stakeholder needs and expectations
- OH&S policy and objectives
- Roles and responsibilities
- How to meet legal requirements
- Audit programmes and criteria
Participation
Involving workers in decisions about:
- Mechanisms for consultation
- Hazard identification and risk assessment
- Actions to control risks
- Competence and training needs
- Incident investigation
Clause 6: Planning
Planning is at the heart of the PDCA cycle. ISO 45001 requires a proactive, risk-based approach.
6.1.2 Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment
Establish processes to identify hazards and assess risks on an ongoing basis, considering:
- How work is organised and social factors
- Routine and non-routine activities
- Past incidents (internal and external)
- Potential emergency situations
- People—including contractors, visitors, and vulnerable groups
- Changes to processes, equipment, or knowledge
6.1.3 Legal and Other Requirements
Maintain a process to identify, access, and evaluate compliance with:
- Health and safety legislation
- Regulations and codes of practice
- Collective agreements
- Voluntary commitments
6.2 OH&S Objectives and Planning
Set measurable objectives that are:
- Consistent with your OH&S policy
- Measurable (or capable of performance evaluation)
- Monitored and communicated
- Updated as appropriate
Don't just measure incident rates. Include leading indicators like training completion, hazard reports, audit scores, and near-miss reporting rates. These help predict and prevent incidents rather than just counting them after they happen.
Clause 7: Support
The support clause covers the resources and enablers needed to implement and maintain your OH&S management system.
7.1 Resources
Determine and provide the resources needed, including:
- People with appropriate competencies
- Infrastructure (equipment, facilities)
- Budget and time
- Technology and systems
7.2 Competence
Ensure workers are competent based on appropriate education, training, or experience. This includes:
- Determining competence requirements for roles affecting OH&S
- Providing training or taking other actions to achieve competence
- Evaluating the effectiveness of actions taken
- Retaining documented information as evidence
7.4 Communication
Establish processes for internal and external communications, determining:
- What to communicate
- When to communicate
- With whom to communicate
- How to communicate
7.5 Documented Information
Maintain documented information required by the standard and determined necessary for effectiveness. Key documents typically include:
- OH&S policy and objectives
- Scope of the management system
- Risk assessments and risk registers
- Legal register
- Training records
- Incident records and investigations
- Audit reports and management review minutes
Clause 8: Operation
The operation clause is about putting your plans into action—implementing the controls identified during planning.
8.1 Operational Planning and Control
Implement controls using the hierarchy of controls:
Elimination
Remove the hazard entirely
Example: Automate a dangerous manual processSubstitution
Replace with something less hazardous
Example: Use water-based paint instead of solvent-basedEngineering Controls
Isolate people from the hazard
Example: Install machine guards or ventilationAdministrative Controls
Change the way people work
Example: Procedures, training, job rotationPPE
Personal protective equipment as last resort
Example: Safety glasses, gloves, hearing protection8.1.4 Procurement and Contractors
Control processes for:
- Procurement of products and services
- Contractors and outsourced processes
- Ensuring OH&S requirements are met
8.2 Emergency Preparedness and Response
Establish processes to prepare for and respond to potential emergency situations:
- Identify potential emergencies
- Plan responses including first aid
- Provide training and drills
- Periodically test and review plans
- Communicate relevant information to workers
Clause 9: Performance Evaluation
You need to check that your management system is working effectively.
9.1 Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis and Evaluation
Determine what needs to be monitored and measured:
- Extent to which legal requirements are fulfilled
- Activities and operations related to identified hazards and risks
- Progress towards OH&S objectives
- Effectiveness of controls
9.2 Internal Audit
Conduct internal audits at planned intervals to verify your system:
- Conforms to ISO 45001 requirements
- Conforms to your own requirements
- Is effectively implemented and maintained
9.3 Management Review
Top management must review the OH&S management system at planned intervals. Review inputs include:
- Status of actions from previous reviews
- Changes in external and internal issues
- OH&S performance (incidents, nonconformities, monitoring results, audit results)
- Adequacy of resources
- Relevant communications from interested parties
- Opportunities for continual improvement
Clause 10: Improvement
The final clause closes the PDCA loop by addressing how to improve your OH&S management system.
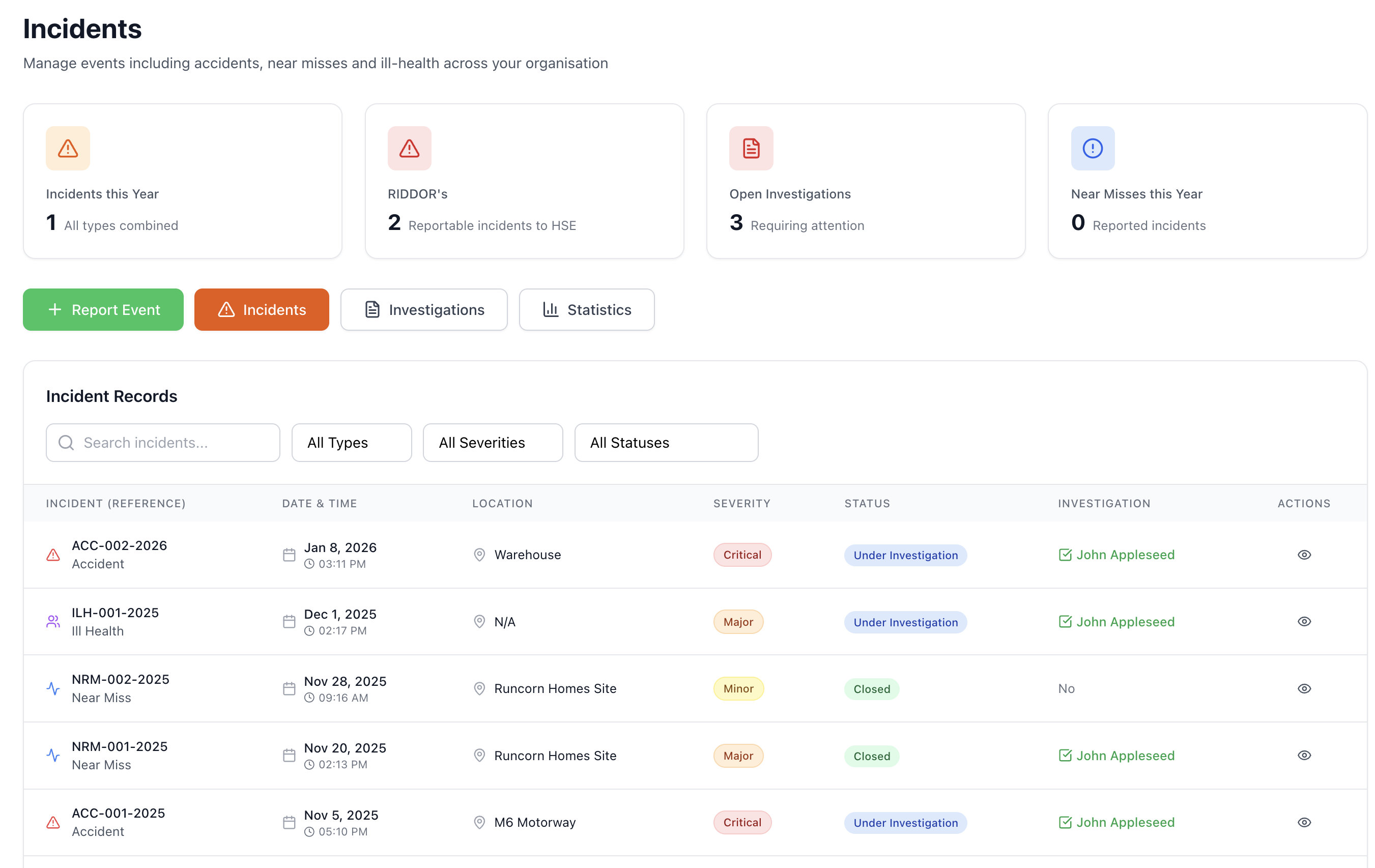
10.2 Incident, Nonconformity and Corrective Action
When incidents or nonconformities occur:
- React to control and correct it
- Evaluate the need for corrective action by investigating
- Determine root causes
- Determine if similar issues exist or could occur
- Implement corrective action needed
- Review effectiveness of corrective action
- Make changes to the OH&S management system if needed
10.3 Continual Improvement
Continually improve the suitability, adequacy and effectiveness of the OH&S management system by:
- Enhancing OH&S performance
- Promoting a culture that supports the system
- Promoting worker participation
- Communicating relevant results to workers
- Maintaining and retaining documented information
Implementation Steps
Here's a practical roadmap for implementing ISO 45001:
Preparation
- Secure top management commitment and resources
- Appoint an implementation team/project manager
- Purchase and study the ISO 45001 standard
- Consider training for key personnel
- Conduct a gap analysis against current practices
Planning
- Define the scope of your management system
- Identify context, interested parties, and their requirements
- Conduct comprehensive hazard identification and risk assessment
- Identify legal and other requirements
- Establish OH&S policy and objectives
Implementation
- Develop and document required procedures
- Implement operational controls
- Establish communication processes
- Deliver training and awareness programmes
- Set up document control systems
Checking
- Implement monitoring and measurement
- Conduct internal audits
- Hold management reviews
- Address nonconformities and implement corrective actions
- Review and improve
Certification (Optional)
- Select an accredited certification body
- Undergo Stage 1 audit (documentation review)
- Address any findings
- Undergo Stage 2 audit (implementation verification)
- Maintain certification through surveillance audits
Common Implementation Challenges
Lack of Top Management Commitment
ISO 45001 specifically requires top management leadership. Without genuine commitment, implementation becomes a paper exercise. Solution: Present the business case, involve leaders in audits, and make OH&S a standing agenda item.
Over-Documentation
Creating excessive procedures that nobody reads or follows. ISO 45001 is less prescriptive about documentation than OHSAS 18001. Solution: Document what adds value and is actually used.
Poor Worker Engagement
Treating workers as subjects rather than participants. Solution: Involve workers from the start, create genuine consultation mechanisms, and act on their input.
Focusing on Certification Over Improvement
Treating certification as the end goal rather than a milestone. Solution: Focus on genuine OH&S improvement; certification will follow.
Resource Constraints
Underestimating the time and effort required. Solution: Be realistic about resources, phase implementation if needed, and use technology to streamline processes.
Conclusion
Implementing ISO 45001 is a significant undertaking, but the benefits—reduced incidents, improved compliance, better worker engagement, and competitive advantage—make it worthwhile. The key is to focus on genuine OH&S improvement rather than just meeting requirements on paper.
Key takeaways:
- ISO 45001 provides a framework for proactive OH&S management
- Leadership commitment and worker participation are essential
- Focus on risk-based thinking and the hierarchy of controls
- Document what adds value, not just what's required
- Use technology to streamline implementation and maintenance
- Aim for continual improvement, not just certification
Ready to implement ISO 45001?
Safety Mate® provides the tools you need to implement and maintain an ISO 45001-compliant OH&S management system—from risk assessments to audits to incident management.
Start free trial